Introduction to Vegan Lifestyle
Definition of Veganism
From a third-person perspective, embracing a vegan lifestyle involves avoiding all animal products, including meat, dairy, eggs, and even honey. It is a conscious choice to exclude animal exploitation for food, clothing, or any other purpose. Veganism extends beyond diet and encompasses a compassionate way of living that respects all beings.Brief History of Veganism
In a friendly tone, the roots of veganism date back to ancient civilizations, but the term was coined in 1944 by Donald Watson. The movement gained momentum in the 21st century, focusing on ethical and environmental concerns, prompting more individuals to adopt this lifestyle.
Health Benefits of a Vegan Lifestyle
Nutritional Advantages
Transitioning to a vegan lifestyle can offer a plethora of nutritional benefits. A plant-based diet packed with fruits, vegetables, nuts, and legumes provides a wide array of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. By focusing on whole foods, vegans often consume more fiber and less saturated fat, promoting heart health and overall well-being.Disease Prevention
Studies suggest that a vegan diet may lower the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. The abundance of nutrients and fiber in plant-based foods can help maintain healthy cholesterol levels and improve blood sugar control, contributing to a reduced risk of various illnesses.
Environmental Impact of Veganism
Conservation of Natural Resources
Entering into a vegan lifestyle not only benefits personal health but also has a significant positive impact on the environment. By choosing plant-based foods over animal products, individuals contribute to reducing their carbon footprint. Livestock farming is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, and by opting for a vegan diet, one helps lower these harmful emissions. Additionally, veganism plays a crucial role in conserving natural resources. It takes far less land, water, and energy to produce plant-based foods compared to animal products, thereby aiding in the sustainability of the planet.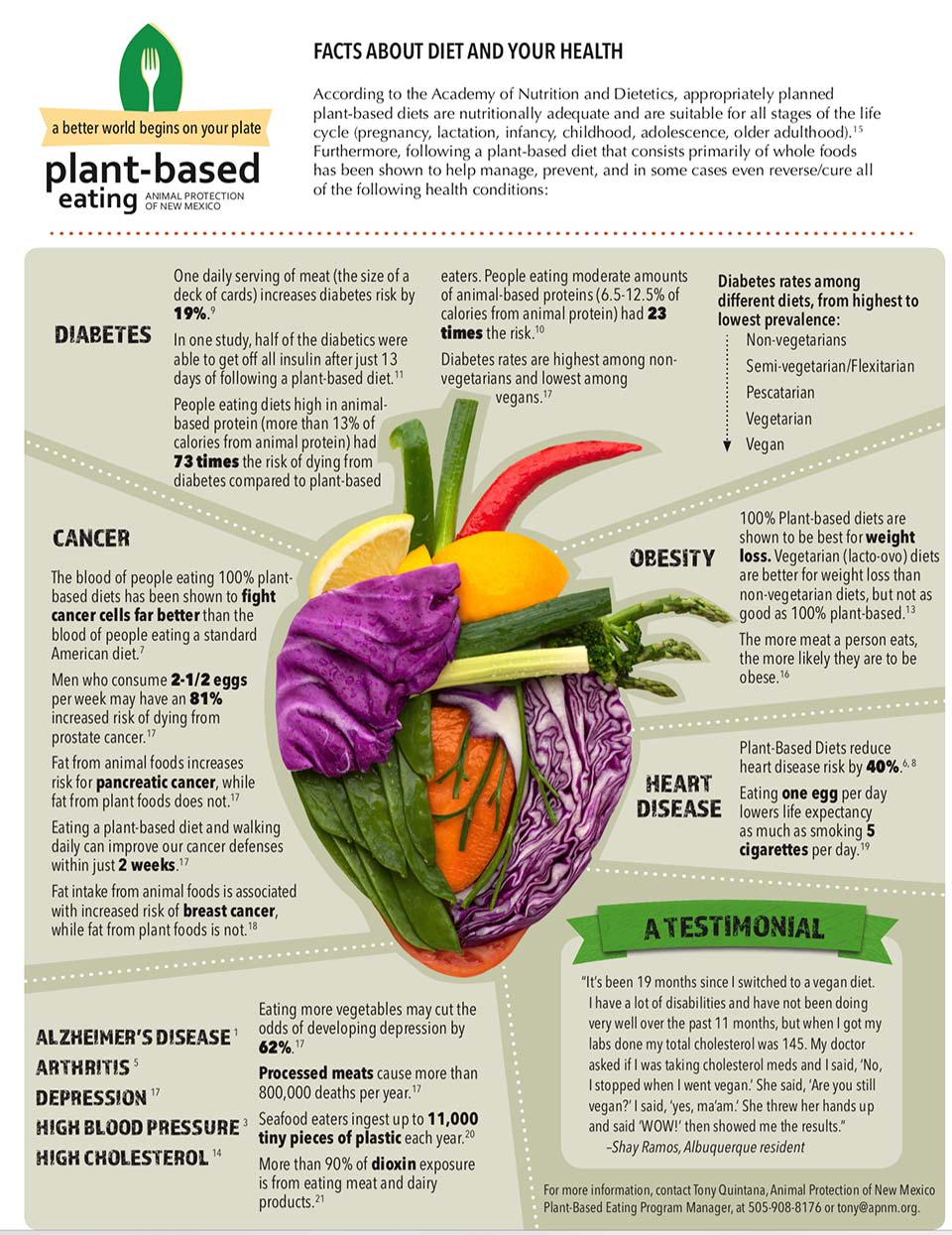
Ethical Considerations in Vegan Lifestyle
Veganism and Social Justice
Entering a vegan lifestyle not only benefits personal health but also has a significant positive impact on the environment. By choosing plant-based foods over animal products, individuals contribute to reducing their carbon footprint. Livestock farming is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, and by opting for a vegan diet, one helps lower these harmful emissions. Additionally, veganism plays a crucial role in conserving natural resources. It takes far less land, water, and energy to produce plant-based foods compared to animal products, thereby aiding in the sustainability of the planet. Veganism embodies ethical considerations that extend to animal welfare and social justice, making it a conscientious choice for both individuals and the planet.
Vegan Diet and Meal Planning
Tips for Balanced Vegan Meals
Exploring a vegan lifestyle not only brings personal health benefits but also positively impacts the environment. By opting for plant-based foods, individuals contribute to reducing their carbon footprint, which is crucial for environmental sustainability. The shift to veganism plays a significant role in conserving natural resources, requiring less land, water, and energy for production. This lifestyle embodies ethical considerations towards animal welfare and social justice. Choosing a vegan diet not only benefits individuals but also demonstrates a commitment to the well-being of animals and the planet as a whole.
Facebook
Twitter
LinkedIn