Introduction to Parkinson’s Disease and Alzheimer’s
Brief overview of Parkinson’s Disease and Alzheimer’s
Parkinson’s Disease and Alzheimer’s are two common neurodegenerative disorders that affect a large number of individuals worldwide. Parkinson’s Disease primarily impacts movement, causing tremors, stiffness, and difficulty with balance and coordination. On the other hand, Alzheimer’s is known for its effects on memory, cognitive function, and behavior. Both diseases can have a significant impact on quality of life and require ongoing management and care.Difference between Parkinson’s Disease and Alzheimer’s
While both Parkinson’s Disease and Alzheimer’s are neurodegenerative conditions, they affect different areas of the brain and manifest in distinct ways. Parkinson’s Disease is characterized by motor symptoms like tremors and muscle stiffness, while Alzheimer’s primarily affects memory and cognitive function. Additionally, Parkinson’s Disease is linked to dopamine deficiency, whereas Alzheimer’s is associated with the accumulation of plaques and tangles in the brain.Genetic Factors
Genetic predispositions in Parkinson’s Disease
Genetic predispositions play a crucial role in Parkinson’s Disease, with certain genetic mutations increasing the risk of developing the condition. Mutations in genes such as SNCA, LRRK2, and PARK7 have been linked to an increased likelihood of Parkinson’s. Understanding these genetic factors can provide valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of the disease and may help in the development of targeted treatments.Genetic risk factors for Alzheimer’s
Similarly, genetic risk factors contribute significantly to the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Variants in genes like APOE are known to increase susceptibility to Alzheimer’s. These genetic factors can influence the age of onset and progression of the disease. By identifying individuals with higher genetic risk, early interventions and personalized care plans can be implemented to manage the impact of Alzheimer’s effectively.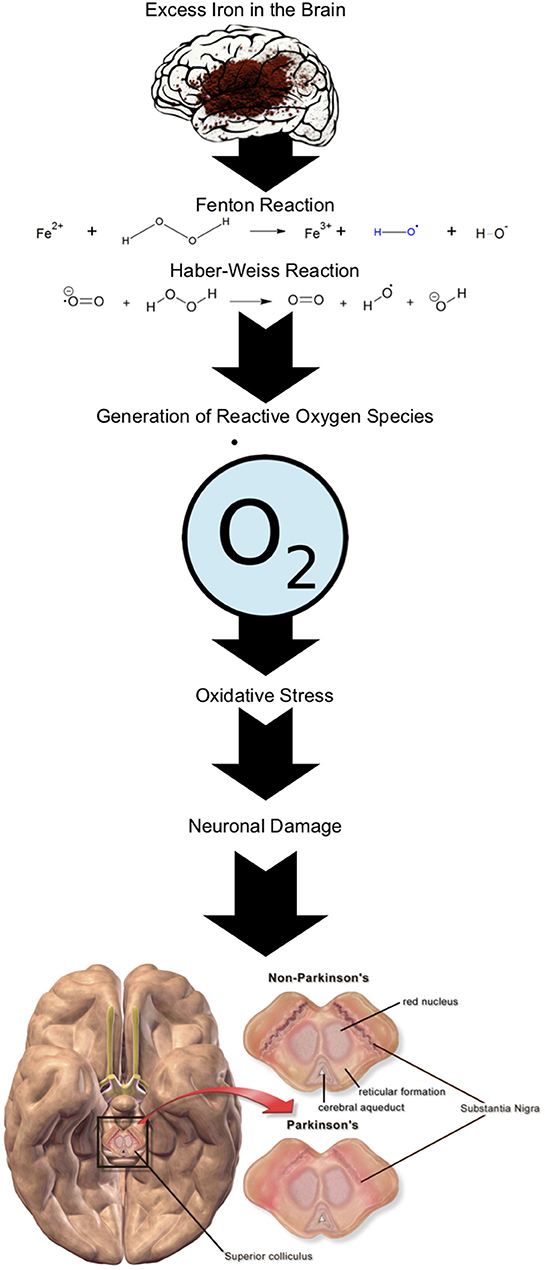
Environmental Factors
Impact of environmental factors on Parkinson’s Disease
Environmental factors also play a significant role in the development of Parkinson’s Disease, alongside genetic predispositions. Factors such as exposure to pesticides, heavy metals, and toxins have been linked to an increased risk of developing the condition. Understanding how these environmental factors interact with genetic predispositions can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the disease’s etiology and progression.Environmental triggers of Alzheimer’s
Similarly, environmental triggers can exacerbate the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in individuals with genetic predispositions. Factors like air pollution, a sedentary lifestyle, and poor diet have been associated with an increased likelihood of developing Alzheimer’s. Recognizing and minimizing exposure to these environmental triggers can play a crucial role in reducing the risk and impact of Alzheimer’s disease.
Neurological Changes
Brain changes in Parkinson’s Disease
Environmental factors, in conjunction with genetic predispositions, significantly impact the development of Parkinson’s Disease. Exposure to pesticides, heavy metals, and toxins has been associated with an elevated risk. Understanding how these factors interact with genetics provides a more comprehensive view of the disease.Neurological alterations in Alzheimer’s
Similarly, environmental triggers can heighten the risk of Alzheimer’s, especially in individuals with genetic predispositions. Factors such as air pollution, sedentary lifestyle, and poor diet increase the likelihood of developing Alzheimer’s. Identifying and reducing exposure to these triggers can help in minimizing the risk and impact of the disease.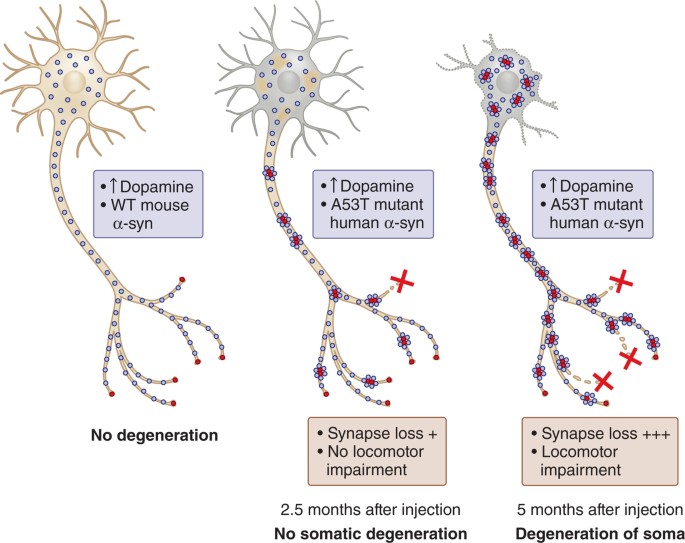
Dopamine Imbalance
Role of dopamine in Parkinson’s Disease
In Parkinson’s Disease, dopamine imbalance plays a critical role in the progression of the condition. Genetic predispositions and environmental factors, such as pesticide exposure, can disrupt dopamine levels in the brain, leading to motor symptoms. Understanding how dopamine is affected in Parkinson’s is crucial for developing targeted treatments and interventions to manage the disease effectively.Dopamine-related implications in Alzheimer’s
Similarly, dopamine imbalances are implicated in Alzheimer’s disease, especially concerning cognitive functions. Environmental triggers like air pollution and lifestyle factors can influence dopamine regulation, affecting memory and cognitive abilities. Exploring the role of dopamine in Alzheimer’s can provide insights into potential therapeutic strategies to mitigate cognitive decline.
Facebook
Twitter
LinkedIn






