Loneliness and Alzheimer’s Disease: Exploring the Connection
Loneliness as a Risk Factor for Alzheimer’s Disease
Loneliness is increasingly being recognized as a potential risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. Research suggests that individuals who experience chronic loneliness may be more susceptible to developing cognitive impairments and neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s. The lack of social interaction and emotional support can have a significant impact on brain health and overall well-being.Loneliness and Cognitive Decline
In addition to its role as a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease, loneliness has also been linked to cognitive decline in older adults. The feelings of isolation and disconnection that accompany loneliness can accelerate cognitive impairment and decrease brain function over time. It is essential to address loneliness as a potential threat to brain health and take proactive steps to promote social engagement and support among individuals at risk.
The Impact of Social Isolation on Brain Health
Social Connections and Alzheimer’s Risk
Research continues to highlight the detrimental effects of social isolation on brain health. Studies suggest that individuals facing social isolation are at a higher risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease due to the lack of social interactions and emotional support. The brain’s cognitive functions may be adversely affected, emphasizing the importance of fostering social connections to mitigate such risks.Effects of Isolation on Mental Well-being
Apart from Alzheimer’s risk, social isolation has been associated with cognitive decline and diminished mental well-being in older adults. The feelings of loneliness and disconnection can accelerate cognitive impairment over time, underscoring the critical need for promoting social engagement to enhance overall mental health and cognitive functioning.Understanding the Mechanisms: Loneliness and Alzheimer’s Onset
Psychological Factors influencing Disease Progression
Social isolation impacts brain health by increasing the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Loneliness triggers biological mechanisms that can lead to neurodegeneration, accelerating cognitive decline. The lack of social connections influences psychological factors, such as depression and stress, that can exacerbate Alzheimer’s progression. Understanding these intricate mechanisms is crucial in developing interventions that promote social engagement to combat the negative effects of isolation on brain health.Research Findings on Loneliness and Alzheimer’s Risk
Contradictory Results in the Scientific Community
Social isolation significantly impacts the onset and progression of Alzheimer’s disease through intricate biological and psychological pathways. Loneliness is known to trigger mechanisms in the brain that contribute to neurodegeneration, hastening cognitive decline. The absence of social connections also influences psychological factors like depression and stress, which can worsen the advancement of Alzheimer’s. Ongoing research continues to provide evidence supporting the link between loneliness and Alzheimer’s risk, although contradictory results exist within the scientific community, necessitating further investigation.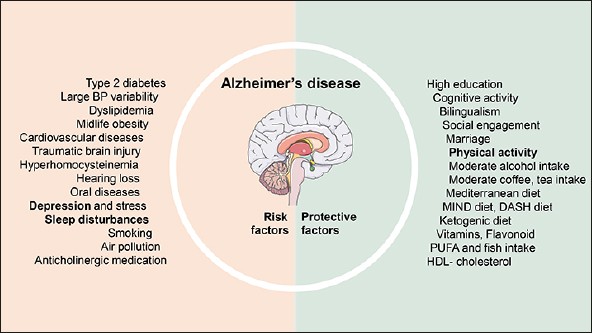
Lifestyle Changes to Combat Loneliness and Reduce Risk
Social Engagement as a Protective Factor
Social engagement plays a crucial role in combating loneliness and reducing the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Establishing strong social connections can help alleviate feelings of isolation, improving overall well-being and cognitive function. By fostering meaningful relationships and participating in social activities, individuals can enhance their mental resilience and protect against the detrimental effects of loneliness on brain health.Healthy Habits for Brain Health
In addition to social engagement, maintaining healthy habits is essential in reducing the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Regular physical exercise, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, quality sleep, and mental stimulation through activities like reading or puzzles are all beneficial for brain health. These lifestyle choices can contribute to cognitive vitality and help counteract the negative impact of loneliness on brain function.
Facebook
Twitter
LinkedIn







