Introduction
Importance of Vitamin B12 in Diet
Vitamin B12 is often dubbed the “energy vitamin,” primarily because it’s crucial for the formation of healthy nerve cells and red blood cells in the body. This vital nutrient helps in the DNA synthesis and keeps our nerves functioning optimally.
A few key points highlight its importance:
- Energy Production: Supports energy metabolism, preventing fatigue.
- Nerve Health: Essential for maintaining healthy nerve function.
- Mental Clarity: Contributes to cognitive health and may prevent memory loss.
Including sufficient vitamin B12 in your diet is essential for overall wellness!

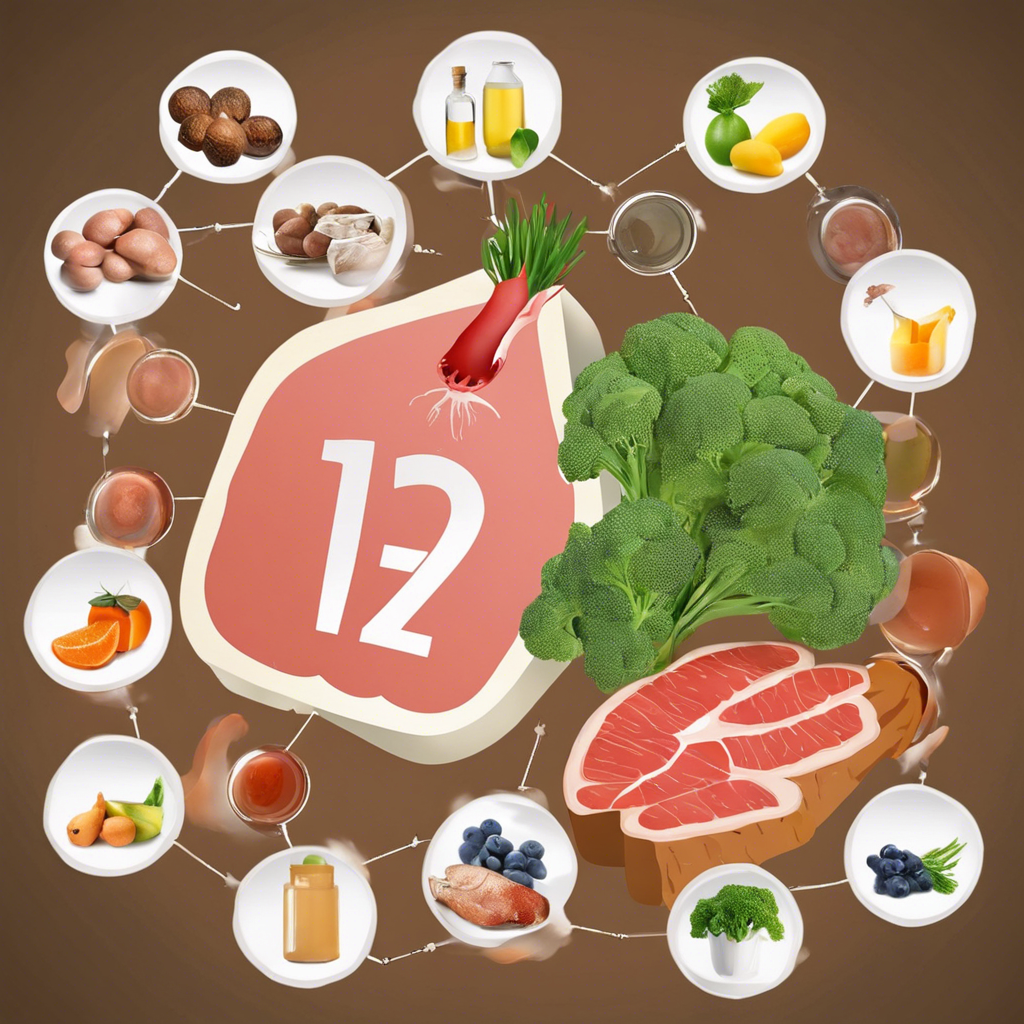
Top 5 Vitamin B12 Foods
Shellfish: Clams and Mussels
When it comes to vitamin B12, shellfish like clams and mussels take the lead. Just three ounces of cooked clams can deliver over 1,000% of your daily requirement. That’s like hitting the vitamin jackpot!
Beef Liver and Organ Meats
Next on the list is beef liver, a powerhouse nutrient. Three ounces provide around 1,000% of your daily B12 needs. For those who enjoy organ meats, this is a delightful and nutrient-dense option.
Fortified Cereals and Nutritional Yeast
For plant-based eaters, fortified cereals and nutritional yeast are fantastic sources. One serving can give you up to 100% of your daily B12. It’s an easy and delicious way to include this vital vitamin in your meals.
Eggs
Don’t overlook eggs! A staple in many households, they offer a good amount of B12. Incorporate eggs into breakfast, whether scrambled or in an omelet, to boost your intake.
Dairy Products: Milk and Cheese
Lastly, dairy products like milk and cheese provide another excellent source of vitamin B12. A slice of cheese or a glass of milk can contribute significantly to your daily needs, ensuring that you maintain optimal health. Enjoying these foods can make a world of difference in your dietary habits!

Understanding B12 Deficiency
Symptoms of B12 Deficiency
Recognizing the symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency is crucial for maintaining your health. Some common signs include:
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or weak.
- Nerve Issues: Tingling or numbness in extremities.
- Mood Changes: Increased feelings of irritability or depression.
- Cognitive Decline: Memory problems or difficulty concentrating.
These symptoms can significantly impact daily life, so it’s essential to pay attention if you notice them.
Risk Factors
Certain individuals are at a higher risk for B12 deficiency, including:
- Vegans and Vegetarians: Limited animal product intake means lower B12.
- Elderly Individuals: Absorption decreases with age.
- Gastrointestinal Conditions: Issues like celiac or Crohn’s disease can affect absorption.
- Medication Use: Some medications can interfere with B12 absorption.
Being aware of these risk factors helps in early detection and prevention of deficiency!

Vitamin B12 Rich Foods in Plant-Based Options
Fortified Plant-Based Milks
For those following a plant-based diet, fortified plant-based milks are a fantastic source of vitamin B12. Brands often enrich their almond, soy, or oat milks with B12, making it easy to meet daily needs.
Tempeh
Tempeh, fermented soybeans, is not only high in protein but can also contain B12 when cultured correctly. It’s a versatile ingredient that can be added to salads, stir-fries, or sandwiches, boosting your nutrient intake deliciously.
Nori Seaweed
Nori seaweed, commonly used in sushi, is another great plant-based option. It contains certain forms of B12, providing a unique way to include this nutrient in your diet. So, consider adding it to snacks or meals for a B12 boost!

Tips for Ensuring Adequate Vitamin B12 Intake
Supplements
For those who may struggle to meet their vitamin B12 needs through food alone, supplements can be a practical solution. Whether in pill form or as sublingual tablets, B12 supplements are widely available and effective. Personalizing the dosage with your healthcare provider is wise for the best results!
Regular Blood Test Monitoring
Additionally, regular blood tests can help monitor your B12 levels, especially for those at higher risk of deficiency. Keeping an eye on your levels ensures you can adjust your diet or supplement regimen as needed—empowering you to take control of your health!
By combining dietary sources with supplements and regular check-ups, maintaining adequate B12 levels becomes much easier and more manageable.

Conclusion
Recap of Top Vitamin B12 Foods
As we wrap up our discussion on vitamin B12, let’s highlight the best food sources once more:
- Shellfish: Clams and mussels are top contenders, providing over 1,000% of daily needs in just three ounces.
- Beef Liver and Organ Meats: A powerhouse for B12, also hitting around 1,000%.
- Fortified Cereals and Nutritional Yeast: Ideal for plant-based diets, offering up to 100% in one serving.
- Eggs and Dairy Products: Simple staples that also contribute to your daily intake.
Final Recommendations
To ensure you’re getting enough B12, incorporate a variety of these food options into your meals. For those at risk of deficiency, consider supplements and regular blood tests. Prioritizing vitamin B12 is a vital step toward maintaining vibrant health and well-being!
 Source: www.netmeds.com
Source: www.netmeds.com