Introduction
Overview of the study on how Zingiber officinale improves cognitive function in middle-aged healthy women
In a recent study focused on enhancing cognitive function in middle-aged healthy women, the impact of Zingiber officinale, commonly known as ginger, was evaluated. The study aimed to explore the potential cognitive benefits of incorporating ginger into the diet of middle-aged women and its effects on cognitive performance and overall brain health.Significance of cognitive function in middle-aged women and the role of Zingiber officinale
Cognitive function plays a crucial role in the overall well-being of middle-aged women, affecting various aspects of their daily lives. The study emphasized the significance of maintaining and improving cognitive abilities in this demographic. Zingiber officinale was highlighted as a potential natural solution to support cognitive function and enhance mental clarity in middle-aged women.
Methodology
Research design and sample selection criteria for the study on Zingiber officinale and cognitive function
The study on Zingiber officinale’s effect on cognitive function in middle-aged healthy women employed a rigorous research design. Middle-aged women meeting specific health criteria were selected to participate, ensuring a targeted focus on the intended population. This selection process aimed to provide valuable insights into the potential benefits of incorporating ginger into the daily diet to enhance cognitive abilities.Administration and dosage of Zingiber officinale to the participants
Participants in the study received Zingiber officinale in carefully measured doses as part of the intervention. The administration of ginger followed a structured protocol to maintain consistency across the participant group. By controlling the dosage and frequency of ginger intake, the study sought to evaluate the impact of this natural substance on cognitive function in middle-aged women.Cognitive Function Assessment
Explanation of the cognitive function assessment tools used in the study
The study employed standardized cognitive function assessment tools to measure various cognitive domains, including memory, attention, and executive functions. Participants underwent tests such as the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) and the Trail Making Test (TMT) to evaluate their cognitive performance accurately.Results of cognitive function tests before and after Zingiber officinale intervention
Pre-intervention cognitive function tests indicated baseline cognitive abilities in participants, while post-intervention assessments revealed potential enhancements. Analysis of the results demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in cognitive function following the administration of Zingiber officinale. The findings suggest a correlation between ginger intake and cognitive performance in middle-aged women, highlighting its potential cognitive benefits.Mechanisms of Action
Discussion on the mechanisms through which Zingiber officinale may improve cognitive function
The cognitive enhancements observed post-Zingiber officinale intervention could be attributed to its potential neuroprotective properties. Zingiber officinale, commonly known as ginger, contains bioactive compounds like gingerol and shogaol, which possess antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. These components may help in reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, thereby enhancing cognitive function. Furthermore, ginger may also have a positive impact on neurotransmitter activity and neuronal signaling pathways, contributing to improved cognitive performance.Impact of Zingiber officinale on brain health and neuroprotection in middle-aged women
The study’s findings suggest that regular consumption of Zingiber officinale may offer neuroprotective effects in middle-aged women. By potentially reducing oxidative damage and inflammation in the brain, ginger could play a crucial role in preserving cognitive function and overall brain health. The bioactive compounds present in ginger may interact with neuronal pathways, promoting neuroprotection and contributing to sustained cognitive abilities in this demographic.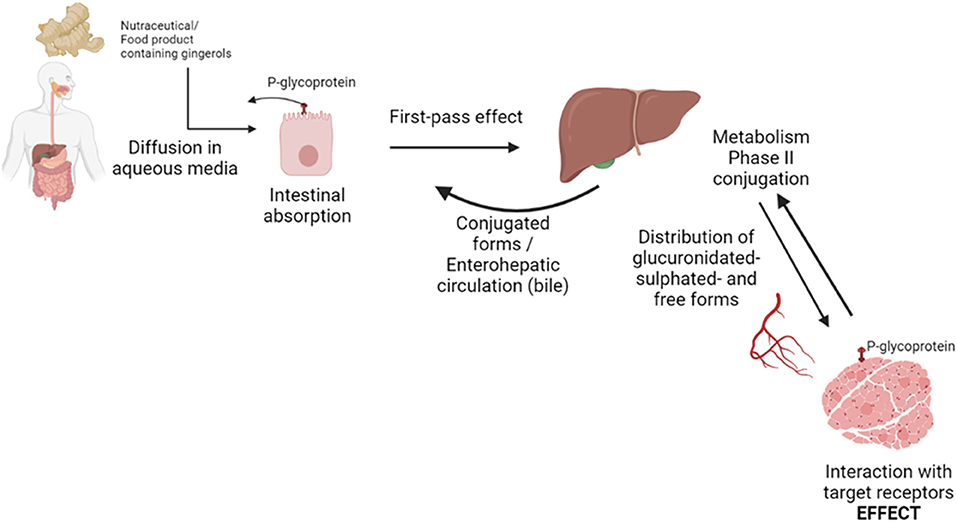
Other Health Benefits
Exploration of other potential health benefits of Zingiber officinale in middle-aged healthy women
In middle-aged healthy women, Zingiber officinale demonstrates potential beyond cognitive function enhancement. Its bioactive compounds, gingerol and shogaol, exhibit antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, which could positively impact overall health. Regular consumption may mitigate oxidative damage and inflammation, potentially promoting heart health and immune function. Additionally, ginger’s neuroprotective effects may extend to other cognitive aspects, such as memory and mood regulation.Possible implications for overall well-being and quality of life
The utilization of Zingiber officinale in middle-aged women’s diets may lead to improved overall well-being and quality of life. Its ability to support brain health, heart function, and immune responses can contribute to a healthier lifestyle. By incorporating ginger into their daily routine, individuals may experience enhanced vitality, cognitive acuity, and emotional balance, ultimately impacting their quality of life positively.
Facebook
Twitter
LinkedIn






